The clap (Gonorrhea)

Contents
What is Gonorrhea?
The clap std or Gonorrhea: (misspelled as ghonorrea, gonorrea, gonorrhoea etc.) A highly contagious sexually transmitted (STD) bacterial infection, sometimes referred to as «the clap». The nickname of the clap refers to a treatment that used to clear the blockage in the urethra from gonorrhea pus, where the penis would be ‘clapped’ on both sides simultaneously.
This treatment is rarely used today, however the nomenclature remains. Gonorrhea is characterized by thick discharge from the penis or vagina. In addition to male reproductive organs & female genital tract, it may infect the rectum, throat, eyes, blood, skin, & joints.
How is Gonorrhea Contracted?
Gonorrhea spreads through semen or vaginal fluids during unprotected sexual contact, heterosexual or homosexual, with an infected partner:
- vaginal or anal sex with an infected partner
- oral sex, although this is less common
- sharing sex toys
- touching parts of the body with fingers (for example, touching the private parts and then the eyes)
- any very close physical contact
- the bacteria can be passed from hand to hand (very rare isolated cases)
- from a mother to her baby at birth
You can NOT catch it from simple kissing, sharing baths, towels, cups, or from toilet seats.
1–14 days.
Symptoms of Gonorrhea
1/2 of women & 1/10 of men who have «The Clap» have no symptoms at all.
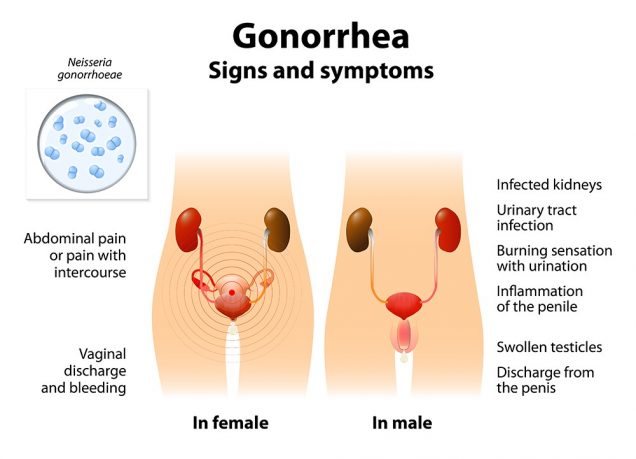
Women’s symptoms can include discharge from the vagina, frequent urination, pain or burning when urinating, & pain between periods. Men are most likely to experience pain during urination & discharge from the penis. The throat infection rarely shows gonorrhea symptoms.
Gonorrhea Symptoms in Women
- strong smelling vaginal discharge that may be thin & watery or thick & yellow/green
- irritation or discharge from the anus
- abnormal vaginal bleeding
- possibly some low abdominal or pelvic tenderness
- pain or a burning sensation when passing urine
- low abdominal pain sometimes with nausea
Gonorrhea Symptoms in Men
- white, yellow or green thick discharge from the tip of the penis
- inflammation of the testicles & prostate gland
- irritation or discharge from the anus
- urethral itch & pain or burning sensation when passing urine
Gonorrhea Testing
A urine test & a swab test — collecting fluid from the penis or vagina by placing a swab in the opening of the urethra; this causes brief discomfort.
- giving a sample of urine
- a genital examination by a doctor or nurse
- taking swabs from the cervix (entrance to the womb), urethra (tube where the urine comes out), throat or rectum
- women may have an internal examination
Gonorrhea Treatment — Is there a Cure for Gonorrhea?
Early treatment is simple & effective, & involves a single dose of antibiotics. In addition, the treatment of chlamydia is also advocated. It is common to have these two STD (Sexually Transmitted Disease) infections together – 50% have both
Treatment of Gonorrhea:
- Cipro® XR 500 mg a single dose, or
- Levaquin® 500 mg a single dose, or
- Tequin® 400 mg a single dose;
Treatment of Chlamydia:
- Doxycycline 100 mg 2–3 times a day for 10–14 days, or
- Zithromax® (azithromycin) 1.0 gm a single dose, or
- Zithromax® Z-pak® (azithromycin) — 500mg on day 1, followed by 1 tab (250mg) once a day for 4 more days
To avoid re-infection, any sexual partners should be treated too.
It’s important not to have unprotected vaginal, oral or anal sex until treatment is completed & the infection has cleared up
Once it has been successfully treated, it won’t come back unless a new infection is picked up.
If «The Clap» Not Treated
Gonorrhea infection can spread through the bloodstream to other parts of the body, causing damage & serious problems.
In women, it can cause:
- life-threatening complications such as ectopic pregnancy (outside the womb)
- blocked fallopian tubes (the tubes which carry the egg from the ovaries to the womb), which can result in reduced fertility or infertility
- long-term pelvic pain
In men, it can lead to:
- painful inflammation of the testicles, which may result in reduced fertility or sterility