STDs list and their Symptoms

Sexually Transmitted Diseases are the ones that are easily passed from one person to another, cause various complications and are sometimes difficult or impossible to cure. This is why it is important to know the most common STDs, their ways of spreading, symptoms and possible outcomes.
They can be caused by bacteria, fungi, viruses, parasites and are often interconnected. Some of them are very similar in symptoms and are hard to distinguish, some favor the development of other sexually transmitted infections.
And although it is impossible to be 100 per cent certain about not contracting one of them at some point, everyone can take preventive measures that will help you reduce the chances of having an STD to the minimum. The basic recommendations are having safe monogamous relations, using condoms when not sure about your partner and having regular visits to a doctor for routine examinations. So here is the list of all most common sexually transmitted diseases.
Contents
- Chancroid
- Chlamydia
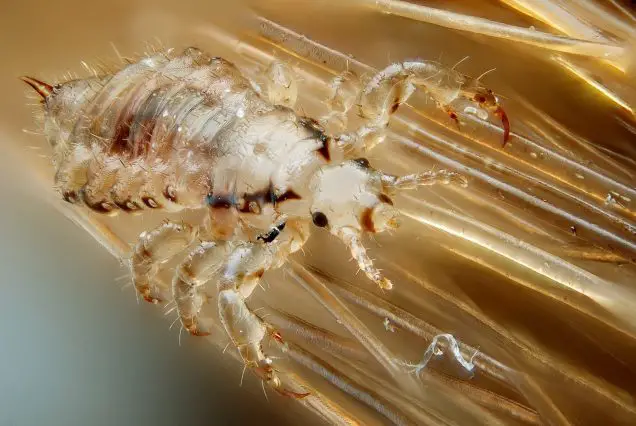
- Crabs (Pubic Lice)
- Gonorrhea
- Hepatitis
- Herpes
- HIV/AIDS
- Human Papillomavirus and Genital Warts
- Lymphogranuloma Venereum
- Molluscum Contagiosum
- Nongonococcal urethritis
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
- Scabies
- Syphilis
- Trichomoniasis
- Vaginal Yeast Infection
- Bacterial Vaginosis
- Yeast Infection in Men
- Balanitis
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
- Mycoplasma
- Mononucleosis (Mono)
-
Chancroid

Chancroid is an infection, uncommon in North America. Transmitted during sexual contacts or through skin contacts, it mainly affects men and causes sores and painful ulcers on penis and other genital areas. Easily cured with antibiotics, Chancroid can lead to complications if untreated. The chances of transmitting the infection get lower when using condoms, however, it should be remembered that it might be enough to touch the skin of an infected person to contract it.
-
Chlamydia

One of the most widespread sexually transmitted infections, Chlamydia can lead to serious complications if not treated timely and efficiently. The infection mainly affects women and may have no symptoms at all. In other cases the infected person may experience abnormal vaginal discharge or urinating discomfort. It is important to locate and take measures as soon as possible before Chlamydia damages the uterus, fallopian tubes, reproductive system, which may end in infertility. Pelvic inflammatory disease is also possible. Like most other STDs, Chlamydia is easily prevented by using condoms and having monogamous relations.
-
Crabs (Pubic Lice)

Pubic lice, also known as crabs, are small parasites residing on genital hair and skin. They may cause itching, irritation, mild fever or have no symptoms at all. It is often easy to spot white eggs or lice themselves with naked eye. They are typically spread during sex or other close skin contacts. It is important to know that condoms do not prevent from crabs’ transmission so it is always better to have a secure and permanent sex partner. Yet, pubic lice are relatively easy to get rid of with the help of medicines.
-
Gonorrhea

Gonorrhea is a widespread sexually transmitted disease, most common among young people under 24. Gonorrhea has few symptoms and is often difficult to diagnose. Men may feel burning during urination, have abnormal discharge from penis or pain in the testicles. Most women do not observe any symptoms, or may also have uncommon discharge and painful urination. The infection needs to be treated immediately as it might lead to genital, rectal or throat infections, as well as develop serious complications, especially in women, including obstruction of the fallopian tubes, infertility or ectopic pregnancy. Gonorrhea (The Clap) is easy to treat on early stages.
-
Hepatitis

Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C lead to liver inflammation and may end up in death. It is typically contracted through body fluids and blood, which makes it easy to contract during unprotected sex or while sharing injection needles with an infected person. The early symptoms may include general sickness, nausea, vomiting, fever or dark urine. If not treated, the disease can develop into chronic hepatitis, hide for a while and lead to cirrhosis or liver cancer. Hepatitis vaccines have become routine for children in many countries. Unvaccinated people, gay men, drug users and even people living together with an infected person are more likely to contract Hepatitis.
-
Herpes

Herpes is one of the most common diseases transmitted through all types of sexual contacts as well as simple touching. Oral herpes can cause blisters or cold sores on the lips, on or inside the mouth. Genital herpes can involve sores, blisters, itching in genital area or even urinating problems. However, most of the times the virus shows no symptoms at all and a person can be unaware of it. There are medicines keeping herpes symptoms subdued and limiting transmission. However, once in your body, there is no cure to get rid of it.
-
HIV/AIDS

Human Immunodeficiency Virus, or simply HIV, is definitely the most dangerous STD. Leading to Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome, or AIDS, the virus does severe damage to immune system which eventually leads to death from any other disease. It is transmitted through blood, vaginal and rectal fluids, semen, and breast milk. Male gay couples and drug users sharing needles are the people particularly exposed to the virus. More than 1.5 million people worldwide die from HIV every year and it is extremely important to take preventive measures to avoid the disease. Having sexual relations with safe and permanent partners and using condoms are the basic rules that will help you keep the virus at bay.
-
Human Papillomavirus and Genital Warts

Human Papillomavirus or HPV is a group of viruses that can lead to warts, genital warts or even cancer. Yet, most HPV types do not cause damage to human body, go away shortly and remain unnoticed. Sexually active individuals are under danger of obtaining the infection with every second person having it at some point of life. Young people are encouraged to take HPV vaccines, preventing from dangerous types of the virus, while women are recommended to pass regular Pap smear tests to control their health.
-
Lymphogranuloma Venereum

Lymphogranuloma Venereum, or LGV, is a relatively rare sexually transmitted disease that becomes increasingly common among gay men in Western Europe, Australia and USA. Caused by several types of Chlamydia trachomatis bacteria, LGV is typically transmitted during anal sex and affects the lymphatic system. The infection may be accompanied by enlarged lymph nodes, rectum inflammation, ulcers, sores or abscesses in genital areas. LGV may be followed by complications if left untreated.
-
Molluscum Contagiosum

Molluscum Contagiosum is a virus, attacking skin, transmitted both sexually and through casual skin contacts, as well as through clothing and towels. Symptoms may include itching and small round bumps in the genital area. The infection is not particularly dangerous and may go away on its own in up to several years. However, it is recommended to treat it to prevent transmission to other people and other parts of your body.
-
Nongonococcal urethritis

Nongonococcal urethritis, or simply NGU, is a sexually transmitted urethra infection, caused by several bacteria, including Chlamydia trachomatis, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Mycoplasma or Trichomonas. Typical symptoms include milky discharge from the penis, burning while urinating. At times there may be no symptoms at all. If left untreated, the infection may spread to testicles, causing pain or even sterility. Protected sex and monogamous relations are the best steps in preventing the disease.
-
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease

Pelvic Inflammatory Disease or simply PID is a serious infection, coming primarily as a complication of untreated Gonorrhea and Chlamydia. The infection affects women’s reproductive organs, such as fallopian tubes, uterus or ovaries. PID may show no symptoms on early stages and, when untreated, can lead to infertility, ectopic pregnancy and other problems. Abnormal periods, vaginal discharge, painful sensations in vaginal area, vomiting and nausea may accompany the infection on later stages. It is essential to maintain safe sexual life and have yourself examined by a doctor on regular basis to prevent PID.
-
Scabies

Scabies is a skin condition, involving intense itching, rash or small bumps, and is caused by tiny parasites digging into skin. An infected person may be unaware of the problem and a visit to a doctor is required to identify the infection. Scabies are easily transmitted during sexual contacts and other skin-to-skin contacts, including sharing bedding or towels. Using condoms is not enough to stay away from scabies.
-
Syphilis

Syphilis is a very dangerous STD, caused by Treponema Pallidum bacterium. It is normally contracted during sexual contacts and often difficult to diagnose. The primary symptoms may include small sores, cuts or bumps on genitals or mouth. Body rash on palms, feet and other parts of the body may follow. When untreated for extensive period of time, syphilis can start destroying body functions and lead to mental, neurological problems, heart diseases, blindness and even death. Infected pregnant women can easily pass syphilis to their children. Moderate sexual life and protected sex are the basic ways to reduce the chances of contracting the infection.
-
Trichomoniasis

Trichomoniasis is another extremely widespread infection, affecting over 8 million Americans annually. It is difficult to diagnose as the infection often doesn’t show any symptoms, especially in men. Women might experience uncommon vaginal discharge, itching or swelling in the genital area, frequent and (or) painful urinating. Trichomoniasis is easily treated, but can also lead to complications, such as vaginitis. Use of condoms can significantly reduce the chances of transmission.
-
Vaginal Yeast Infection

The vaginal yeast infection is caused by a fungus in the vaginal zone. It is a very common issue. They produce a lot of noise with discomforts like rashes, tingle, soreness, and itching. However, most are not as severe as they feel. The yeast guilty of charge when you have a yeast infection is called Candida Albicans. When they proliferate above the regular levels, then the symptoms arise. The solution is to restore the balance inside the vagina. That way, those unwanted fungi get back to normal. You can get antifungal creams without prescription to get rid of the problem. -
Bacterial Vaginosis

The vagina is full of bacteria. When everything is ok, it is mostly good bacteria. However bad bacteria can turn things upside down, causing Bacterial Vaginosis. This kind of problem usually occurs to women who have sex on a regular basis, and with different partners. Most times it is asymptomatic, and when it has symptoms, it is just a vaginal discharge with a particular smell. Sometimes it is so slight that women don’t notice it. The lightest problems disappear in few days without any treatment. Severe issues require a treatment that is given in the form of an antibiotic. -
Yeast Infection in Men

Yeast infections are common in women, but men can also suffer from a yeast infection in the genital area. The Candida Albicans yeast is responsible for such problems. They can occur when you practice unprotected sex with a woman who has a vaginal yeast infection, which is produced by the same fungus. However, there are other risk factors. There is a certain amount of yeast that is normal. An over development is what causes problems. The symptoms are itchiness and redness in the penis area and even some pain. Treatment is easy, but you need an accurate diagnose. -
Balanitis

Balanitis is a disease that affects your penis. This problem is common in men who are not circumcised. The flaps of the skin covering the penis tip should be clean to prevent the disease. This infection attacks commonly people who have diabetes, reactive arthritis, or the Reiter’s syndrome. It can also be the result of an allergic reaction to certain drugs like aspirin or tetracycline. The infection manifests itself with swelling, itching, and redness. Pain is also common and discharges at the tip with smegma and a bad smell. The worse cases cause pain when peeing and erection problems. -
Cytomegalovirus (CMV)

The Cytomegalovirus or CMV is an infection transmitted through a virus. Anybody is at risk. It can be infected through all sorts of fluids, from saliva to urine, semen, blood, and breast milk. Once you get the CMV virus, there is no turning back. If you are in perfect health, it usually remains dormant, and you will experience no problems at all. However, when your defenses are weak, or if you suffer other health conditions, the Cytomegalovirus can cause further complications. Even newborns could grow perfectly fine. Go to your doctor to get proper treatment and get plenty of rest. -
Mycoplasma

Mycoplasma is a form of bacteria attack. There are several types of Mycoplasma (over 100), depending on their development area. Their modus operandi is to get into the membrane of each cell. As a one-cell organism, they live by feeding on their carrier cell. One of the most common types of Mycoplasma is the Mycoplasma Genitalia. It infects the genitourinary tract of both men and women. When it is combined with Mycoplasma Pneumoniae, the consequences affect the whole body. It is the root cause of severe infections in the respiratory system. Other issues include heart problems, prosthetic issues, joint pain, and upset of the central nervous system. -
Mononucleosis (Mono)

Mononucleosis or simply Mono is a disease caused by the EBV (Epstein-Barr Virus). It is spread through the saliva, nose fluids, and tears. This is not a serious problem, except for those who have a weak immune system. Most people have it, and few know it. The symptoms are vague and commonly confused with the common flu. They include tiredness, sore throat, swollen glands, general weakness, fatigue, and at times even a high fever. A blood test can confirm the diagnosis. The most common way of contagion is to kiss other people. Other ways to get it is by sharing glasses, toothbrush, or spoons.