Crabs STD (Pubic lice) pictures and images

Pubic lice (Phthirus pubis) are small parasitic insects that are found primarily in the pubic area or genital area of humans. There occurs a set of symptoms caused by infection with pubic lice. The bite of pubic lice irritates skin, in medicine it is known as pediculosis pubis (It is also known as “crabs std”).
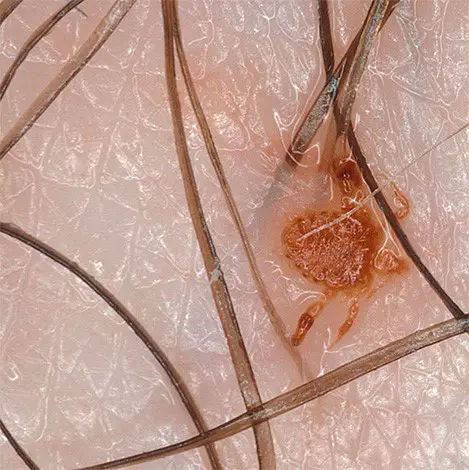
The manifestations of pubic lice infection does not appear immediately. The characteristic symptoms of pubic lice infection appear a few weeks after infection. For this reason, a person infected with pubic lice can infect other people for a long period of time without even knowing about it.
Poor personal hygiene is not related to the spread of pubic lice. Pubic lice not only infect a person living in unsanitary condition, but also a clean suited and well-groomed person. The person who maintains the basic rules of hygiene and the person who doesn’t maintain, both have the same chance of getting infected by pubic lice. In a word, pubic lice can infect any person.
The appearance of the pubic lice is totally different from head lice. Their way of life also differs from each other. These two totally different types of blood-sucking insects are incapable of interbreeding. As these two insects are different, the treatment approaches for fighting pubic lice have their own characteristics.

Crabs STD Prevention >>>
Appearance of pubic lice
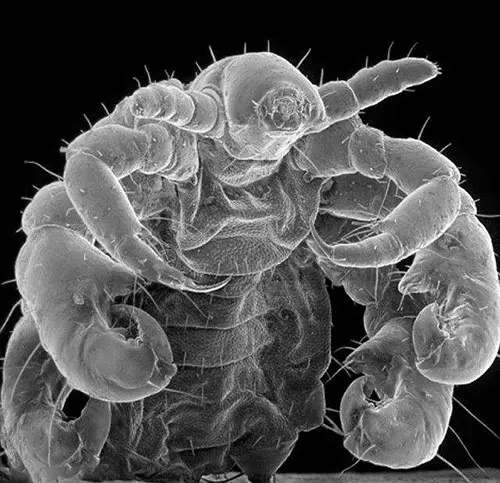
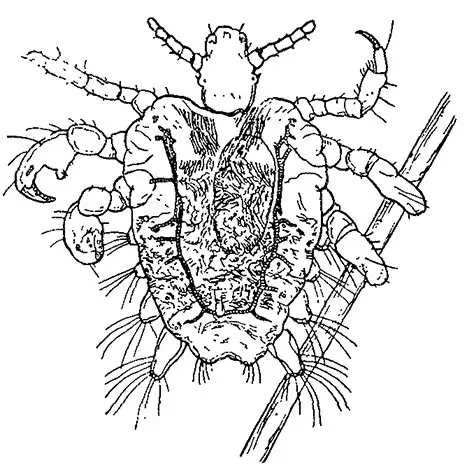
Pubic lice usually have three forms. They are – the eggs (also known as a nit), the nymph and the adult lice. The pubic lice are smalls insects which have a light brown color in external appearance. Sometimes the adult lice have a yellow-grey or dusky red color. The length of an adult louse is about 2 mm, in larvae it is -0.7 mm. The pubic lice have strong and massive legs. When the legs are placed in the sides , the pubic lice seem to have a greater width than their length.
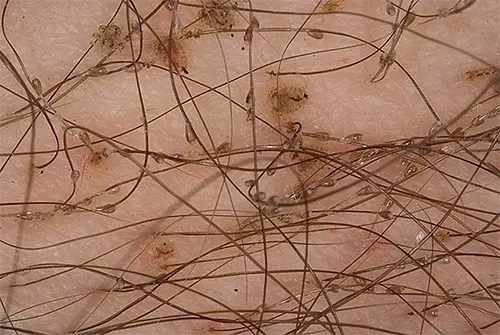
As the color of pubic lice is slightly brown , they are hardly noticeable on the hair. It gets further enhanced by the overall structure of the hair on this part of the body.
In the photo – How pubic lice look on the hair
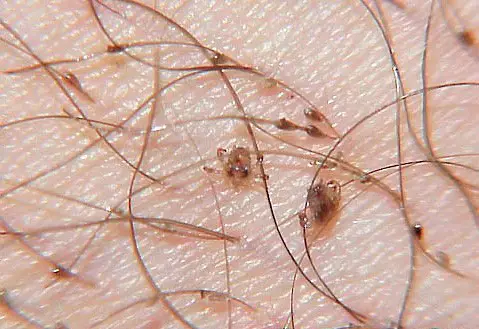
On the next photo – a pubic louse under a microscope at a large magnification

When seen through naked eye, it is very difficult to identify the pubic lice on hair by its appearance. The lice look like a small seal on the hair. Along with this, they inhabit near the base of the hair which make them less conspicuous.
Pubic lice have strong paws like “crabs”, these paws have claw like appearance in the ends which enables the pubic lice to hold on to hair easily. Besides, the pubic lice have such an unique body shape which is very much helpful for them to press themselves against the hair. The lice are adapted to retain on hair.
The massive paws help the pubic lice to move quickly along with skin surface. They move quick enough to look for a biting place on the skin.
In the photo: you can consider the details of the body structure of the pubic lice
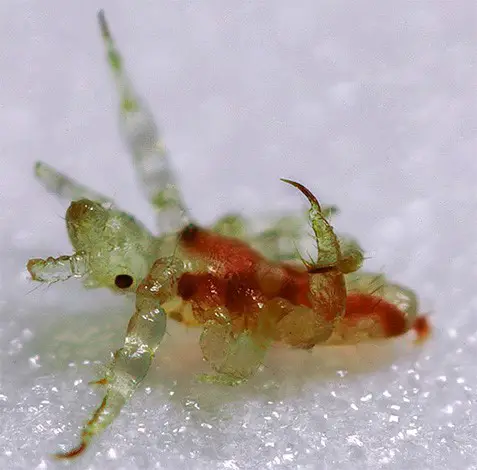
Adult pubic lice are much bigger than the larvae. The larvae are measured half a millimeter in length in their early stages of development.
In the photo: Clear view of a larvae of the pubic lice look when magnified under a microscope

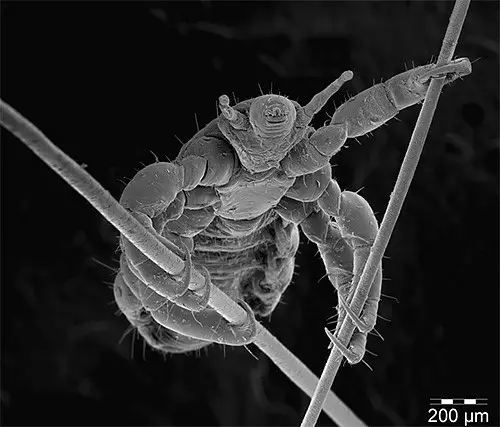
Pubic lice are totally different from other human parasites. They bite in the pubic region. Among the other human parasites, only mites bite in pubic region. But mites can be differentiated from pubic lice, because mites are large parasites. Pubic lice can move through hair which mites can’t. Pubic lice have three pairs of legs , on the other hand mites have four pairs .

Bed bugs are much larger in comparison to pubic lice. The pubic lice have no wings or powerful jogging paws like the other insects. As a result they move usually by crawling.
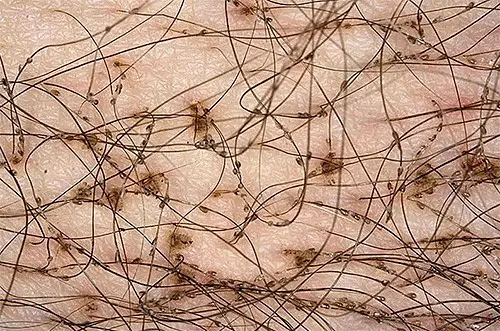
Here are a few photos of pubic lice

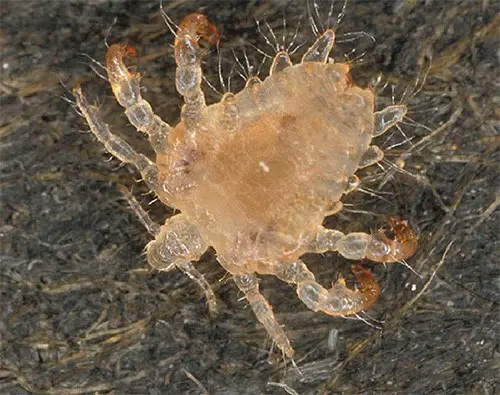
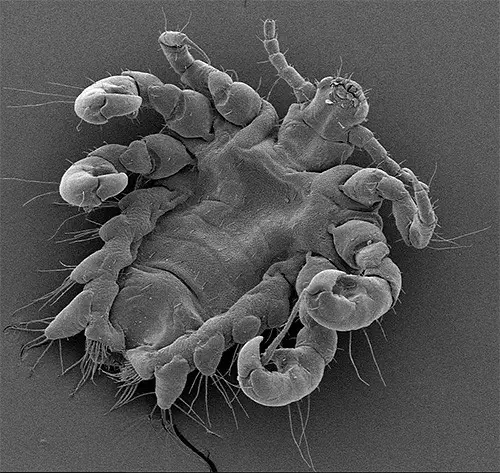
Under a microscope we can see the “crabs” like characteristic features of pubic lice. After seeing the characteristics features if somebody thinks that he/she will be able find out pubic lice in their hair, they are totally wrong. Because it very much difficult to identify the pubic lice in the hair because of their very small size. Sometimes people ignore the small dark dots on their hair, which might have been pubic lice.
The photo below shows how pubic lice look without increasing, under normal conditions
Lifestyle of pubic lice
Parasites lives everywhere around us. Such as- they live in the waters, furniture, garbage or any other natural surroundings. But, pubic lice only live on human body. Pubic lice need human body for their existence, because they live on human blood. They have adapted their body structures to adhere themselves constantly in the human body, and they never leave the hair of human body. If they fall off, they die after 1 to 2 days.
The photo below shows pubic lice

If a louse for some reason is removed from the pubic hair and falls on the bed or in a natural setting, it is likely to die in a few days from hunger. In exceptional cases, if a naked person appears in the same place, the parasite can creep onto it. Usually, lice are rather inactive and they can not find a new master by long-distance movements.
The pubic lice can only survive on human body. They breed and multiplies there. Animals do not get or spread pubic lice. One can get infected by pubic lice only from another person.
Pubic lice live on coarse human body hair. They not only live on pubic hairbut also on Hair on the legs and armpits, eyebrows and eyelashes. Pubic lice do not parasitize on beard, moustaches, chest hair and scalp hair.
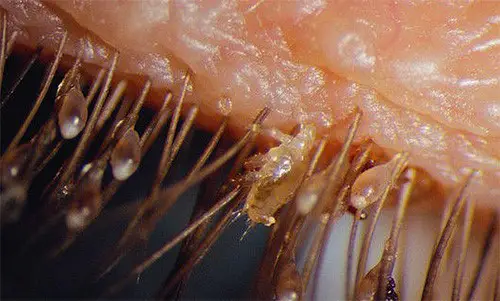
Pubic lice feed on human blood. They have small styloid-like outgrowths in their mouth. With the help of these outgrowths, they pierce the skin and get to the blood vessels. After puncturing the vessel walls, the lice expand their esophagus and suck blood like a pump. During the sucking of blood the parasites injects some special enzyme into the wound which prevent blood clotting and facilitates the blood flow into the parasite’s stomach.
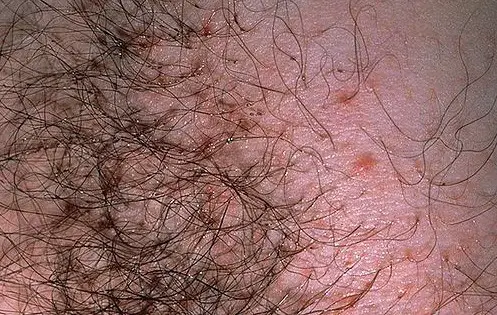
When the parasites pierce the skin, a person feels a very light prick. The enzyme secreted by the parasite causes itching like a mosquito bite. The enzyme also causes slight tissue swelling in the bite area. This itching is the most common symptom of pubic lice.
In the photo: you can see the photo bites of pubic lice
The pubic lice feed on blood at every 4 to 5 hours interval of a day and each time the lice suck out about 0.5 mg of blood. A louse can’t remain hungry for a long period of time. The pubic lice die after 1 to days of hunger strike.
30 to 31 ° C is the optimum temperature for the reproduction and development of pubic lice. If the temperature is below 20 ° C and above 40 ° C, the development of nits (lice eggs) ceases and the adult lice do not reproduces. Lice and nits can survive for week if the temperature is around 1 to3 ° C. The parasite will die immediately within half an hour if the temperature is below -5 ° C and above +55 ° C
Pubic lice have reduced eyes. Normally they do not see anything. Their orientation is done by smell.
Pubic lice can survive in moist air. In dry air, their mobility is lost and they easily fall from the hair. This technique is used in American Health facilities, they treat the pubis of infected people with air from hair dryer with a temperature of about 50 ° C. and the parasites fall off after combing.
Reproduction of pubic lice
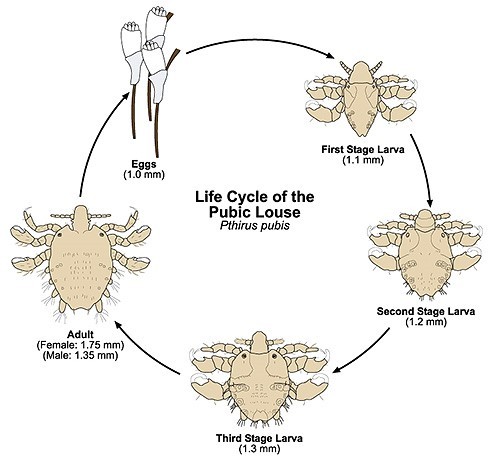
Pubic lice reproduce very rapidly. Under suitable conditions, it takes about 16 days to complete the whole life cycle of the parasites.
- It takes 5-7 days for the development of the egg.
- The larva develops within 13 to 17 days, during this time, approximately at equal intervals, it experiences three molts
About noon an adult female is needed to free itself after molting from the larva shell, drink blood, mate with the male and lay off its first egg.
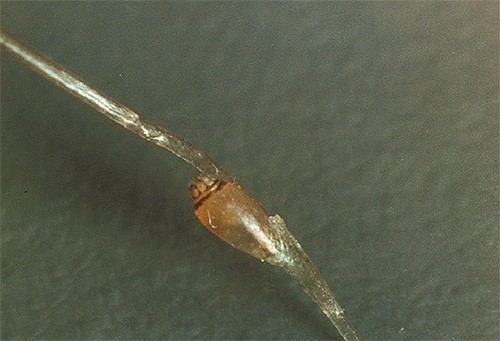
Eggs of pubic lice are known as nits. They are like a capsule which is firmly attached to the hair. They keep a distance of 1-3 cm from the surface of the skin. The nits have a lid and a small foot. With an unaided vision, louse eggs look like small light-colored dots on the hair. In length, the eggs reach 0.5-0.6 mm length and have an almost round shape.
Larvae of head lice are externally similar to adult insects and are therefore called nymphs. They also feed on blood and lead the same lifestyle like the pubic lice. The main difference lies between them only in small sizes and lack of external genitalia.
Under a microscope, the nits of pubic lice are different from nits of head lice. In the latter the eggs have an elongated, spindle-shaped shape. The photographs show the difference between the nits of pubic lice from eggs of head lice

Each female lays 1 to 3 eggs per day. During all of its short adult life (sexually mature insect lives 20-30 days, in rare cases – up to 40), each female lays 30 to 50 eggs.
What could be the dangers of pubic lice
Unlike head and other body lice, pubic lice almost never carry infectious diseases. However, even their natural activity is already enough to cause a lot of unpleasant symptoms and consequences. Such as
- Itching and bite marks
- Bluish spots on the bite sites. These are the reaction of the skin to enzyme produced by the lice
- Papules and pustular inflammation at the site of combed bites, in especially neglected cases growing into pyoderma
All these symptoms in the complex are called pediculosis pubis.
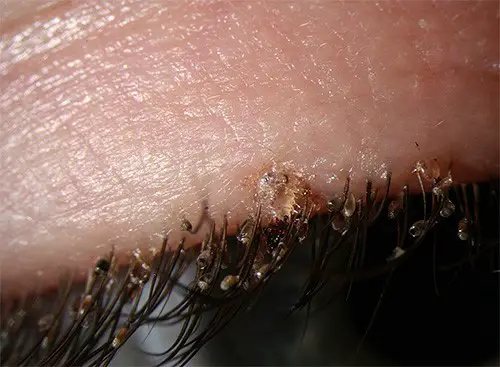
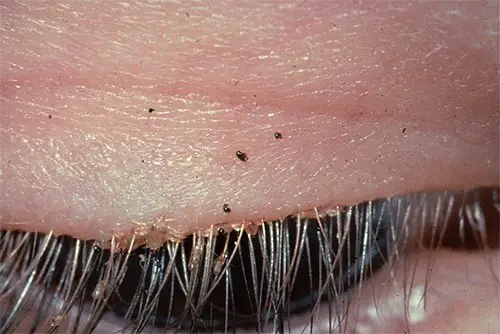
Infection of the eyelids and eyebrows with pubic lice can lead to the development of conjunctivitis and blepharitis.
In the photo below, you can see how the pubic lice infected eye lids looks like
Methods of transmission of pubic lice and general epidemiological situation
Pubic lice are most commonly transmitted during sexual acts, crawling from the hair of an infected person to hair of a non-infected one. Pediculosis pubis is a sexually transmitted disease, which is equally common in both sexes. Pubic lice in men are as common as in women. They can also affect children.
In recent decades, scientists have noted a reduction in the number of cases of pubic lice infection due to the entry into the fashion of shaving pubic hair. Another century or two ago, pubis was shaved mainly by female workers of the ancient profession precisely for protection against lice. Today, with the cult of the hairless body, pubic lice are deprived of their habitats.
Pubic lice can survive up to two days in water and therefore in very rare cases are transmitted in swimming pools and open water between bathing people.
In general, pubic lice are most common in third world countries, especially in Africa, where unhygienic and promiscuous sexual relations reign.
It is the frequent change of sexual partners that is the cause of infection by pubic lice, and due to the fact that within a month after infection a person does not feel the signs of pediculosis pubis, he/she can silently infect other people. For this reason, lice can successfully spread even in a society with a high level of sanitation.
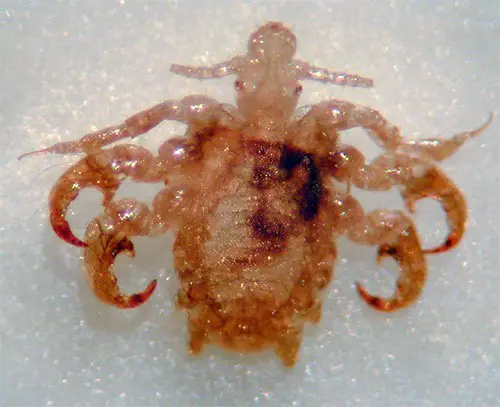
Here are some more photos of pubic lice

How to get rid of pubic lice
The most simple and effective way to destroy pubic lice is to shave the hair at the site of their dislocation. This procedure takes half an hour and guarantees complete disposal of parasites.
Dealing with head lice is comparatively difficult.

We fight against it with the help of special shampoos and ointments. Such remedies should contain powerful insecticides such as Cypermethrin or Deltamethrin, which have a nerve-paralyzing effect on parasites, but are harmless to humans. When the first treatment of hair with such a preparation, active adult insects and larvae are destroyed, and in a second treatment, after a week, those larvae are destroyed which were hatched from the surviving nits.
In order to avoid infection with pubic lice, casual sexual intercourse should be avoided. For complete reliability, you can regularly shave your pubic hair, thereby protecting yourself from potential transmission of parasites.
