Gum infection: Gingivitis and Periodontitis
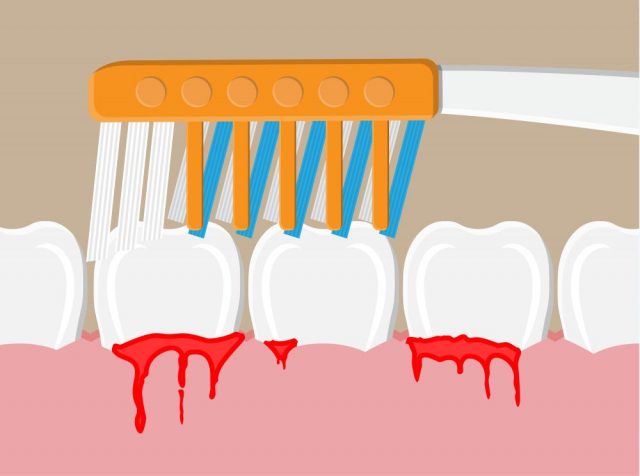
Gum infection or disease also known as periodontitis is an infection of the tissues holding the teeth in place. It is caused by poor flossing and brushing habits that make it possible for a sticky film of bacteria known as a plaque to build up on the teeth and harden. When not properly treated, gum infection could sometimes lead to painful chewing problems, bleeding, sore gums, and tooth loss due to the destruction of tissues surrounding the teeth.
Problems associated with gum infections
Gum infection is an infection that has a high risk of spreading its damage to vital areas of the body like the brain. An infected gum may damage the jaw bone and even cause teeth to fall out. The infection may spread through blood vessels to the brain which will lead to a brain abscess, and in very severe cases, it could lead to the patient going into a coma. It could continue spreading upward and may eventually cause a sinus infection.
Furthermore, a lot of women have swollen, tender, red and bleeding gums whenever they floss or brush during pregnancy. When gum inflammation occurs during pregnancy, it is termed pregnancy gingivitis which is a mild form of gum infection. Pregnancy gingivitis causes the gums to be hypersensitive to the bacteria in plaque, and this is due to hormonal changes. It is very unlikely for pregnancy gingivitis to be harmful to you or your baby especially if you maintain good dental hygiene. Gum infection may only cause preterm labor in women who have a severe case of gum infection.
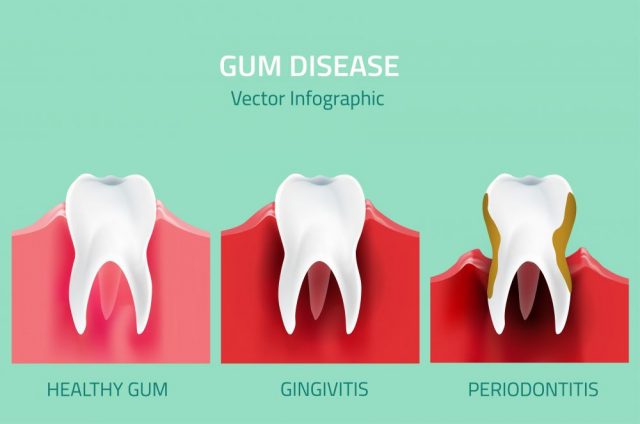
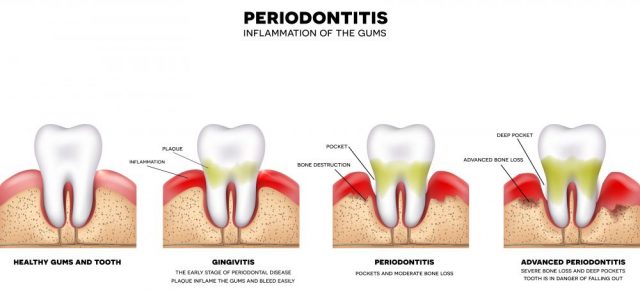
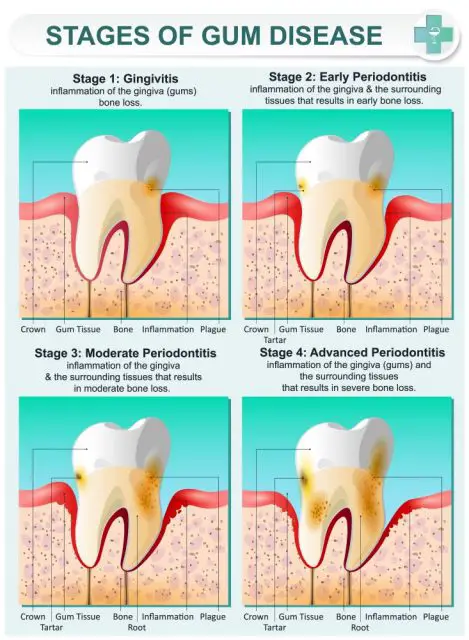
What is the difference between gingivitis and periodontitis?
Gum inflammation, known as Gingivitis is like a precursor to periodontal disease. It usually starts before gum disease, but not all gum inflammation ends up as gum disease. At the stage of gum inflammation, irreversible tissue or bone damages have not occurred.
Gum inflammation will most likely lead to gum disease whenever left untreated. The inward part of the bone and gum of a person living with gum inflammation gently pulls itself away from the teeth leading to the formation of pockets. The little pockets of spaces between gums and teeth become infected as a result of the collection of debris.
The hole continues to deepen with more bones and gum tissues being destroyed as the disease develops. As this continues to happen, the teeth are no longer fastened well in place, and they become slack after which tooth loss starts.
What are the causes of gum infection?
Although other factors may cause gum disease, the main cause of gum infection is Plaque.
Some of the other factors that may contribute to gum disease include
- Illness
Different illnesses may negatively affect the health of your gums. Diseases like HIV or cancer that meddle with the health of your immune systems are major culprits. Patients living with diabetes are at an increased risk of getting different infections such as cavities and periodontal disease. This is essentially because diabetes affects the body’s ability to use blood sugar.
- Bad habits that affect teeth health
Bad habits like smoking may also make it pretty hard for gum tissues to repair itself.
- Medications
Certain medications reduce the production of saliva in the mouth and saliva is known to have a protective shield on gums and teeth.
Another salient contributing cause of dental disease such as gum inflammation is family history.
- Bad oral hygiene practices like flossing and brushing daily put one at a higher risk of developing gum inflammation.
- Hormonal changes just like those that happen during pregnancy, menopause, puberty and monthly menstruation cause the gums in the mouth to become extra sensitive. This makes it very easy for gum inflammation to develop.
Symptoms of gum infection
A lot of times, gum infections develop showing only a few symptoms but without causing pain and this may continue till when the disease is fully developed. While the symptoms caused by periodontal disease may be subtle, the condition isn’t entirely without any warning signs. Some of the symptoms of periodontal disease may be caused by an underlying disease. Possible symptoms of gum infection include;
- Receding gums
- Tender, red and swollen gums
- Bleeding gums before and after brushing one’s teeth
- Bad breath and taste
- Shifting or loose teeth
- Development of deep holes and spaces between gums and teeth
- Scattered teeth and changes to the arrangement and fitting of the teeth.
In some cases, you might not notice any sign or symptom, but you may still have some level of periodontitis. Gum infection may cause changes in just one particular tooth like the molars, in some people. It is the job of a periodontist to recognize and evaluate the development of gum infection.
Prevention
The growth and development of gum disease can be avoided, and gum inflammation could also be treated in many cases as far as you take adequate care of the plaques. This means professional cleansing of your dental cavity about two to three times a year and consistent flossing and brushing. Brushing helps to eliminate plaque from your teeth from areas that are easily accessible, and flossing can be used to remove plaque and food particles hiding beneath the gum and in between the teeth. Antibacterial mouth rinse could also be used to reduce bacteria in the mouth that could lead to plaque and by extension gum infection.
While it is possible, it is only in rare cases that you have gum infections after deep cleaning. It is, however, important to let your dentist know you have other gum or teeth problems if this happens. Deep cleaning of gums is important because bacteria cause infections and prophylaxis always give more benefits than problems in a bid to keep your oral health at an optimal level.
There other lifestyle and health changes that could be made to help decrease the severity, risk, and speed of development of periodontal disease. Some of them include
- Reduce stress
It may be more difficult for your body’s immune system to fight off infections if you are regularly stressed, so you have to manage and reduce stress.
- Stop smoking
Smoking is a major factor contributing to the development of gum disease and smokers are said to be at a higher risk of gum infection than people who don’t smoke. Smoking could even reduce the chances of getting treated successfully.
- Avoid grinding and clenching your teeth
As much as possible, do not clench or grind your teeth as these may put excess and unnecessary force on the tissues supporting the teeth. This could then increase the possibility of the tissues being destroyed.
- Maintain a balanced diet
One of the things that help the immune system fight infections is proper and balanced nutrition especially foods that have antioxidant properties.
However, it is possible to practice good oral hygiene, effect healthy lifestyle changes and still have a high risk of having gum disease as a result of heredity. You may be at a higher risk of having gum infection if anyone in your family has gum disease. Frequent cleanings, checkups, and treatment are often recommended for people that are at a high risk of having gum infection to take care of the condition better.
Diagnosis
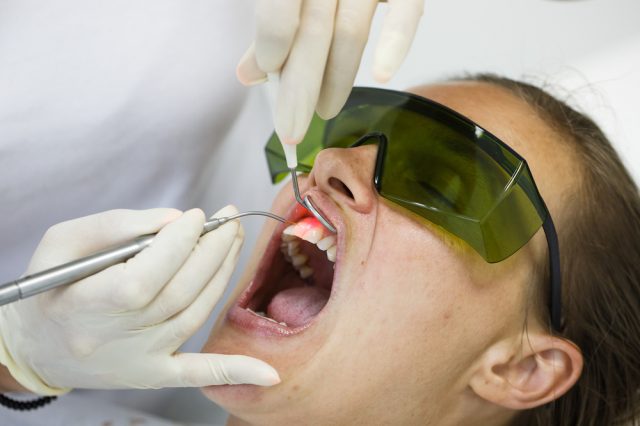
When you get an appointment with a dentist for diagnosis, your dentist examines your gums and notes any signs or symptoms of gum inflammation. He/she makes use of a tiny ruler known as a probe to evaluate and measure the if there are any pockets or holes around the teeth. The depth of pockets in a healthy mouth is usually between 1 and 3 millimeters.
Your dentist may also ask about your medical history to identify risk factors or conditions like diabetes, smoking or cancer that may contribute to periodontal disease. The dentist may also order an X-ray to check if or not there is any bone loss.
Gum infection treatment and pain relief
The idea behind treating gum disease is mainly to promote the reattachment of healthy gums to teeth. Gum disease is also treated to stop the progression of the disease; reduce swelling, the depth of pockets and the risk of infections.
Treatment is the only way to relieve pain associated with a gum infection. In its early stages, gum infection may be reversed with topical or oral antibiotics, better personal hygiene practices, and professional deep cleaning. Gum infections in its latter stages may require surgical intervention to open up the inflamed pockets of tissue, stabilize shaky teeth and repair bones that are already damaged.
Traditional treatment
Some examples of possible ways to treat gum infections conventionally include
- Routine cleaning
- Prescription antibiotics
- Prescription mouthwash
- Deep cleaning
- Gum grafting surgery
- Root canal therapy that involves the placing a permanent crown there
Treating a gum infection without antibiotics
When gum infections need to be treated without the use of antibiotics, there are home remedies that could be used. These home remedies are affordable, simple and straightforward. The best route to treating gum infection is to start with proper preventive care.
- Brush properly at least twice a day and focus on the gums
- Floss properly, cleaning in between your teeth with toothpick, floss or water flossing
- Symptoms of gum infection can be alleviated too by rinsing your mouth with warm and salty water.
- Make use of essential oils in water as a mouth rinse or on your toothbrush
Home Remedies for Treating Gum Infections
Home remedies also exist for treating gum infections. These home remedies may help to deal with the symptoms associated with the infections and also maintain quality oral health.
- Salt Water
One good way to relieve pain and discomfort due to gum infection is to rinse or gargle your mouth with salt water. Two teaspoons of salt in one glass of lukewarm water is enough to help you practice this about two times a day.
- Tea Bags
Tea is known to contain tannic acid. Tannic acid is known to be good at helping to relieve pain caused by gum infection. It is more effective to apply a tea bag to your gums that to gulp down the tea. Insert a tea bag into a cup of boiling water and remove it after a few minutes, allow it cool and then apply the tea bag to the infected gums. Keep the tea bag there for about five minutes and continue the process about two times daily and it will bring relief.
- Honey
Honey is generally known as a natural antibacterial. It can also be used in the treatment of infected gums. Rub a small amount of honey on the infected gums immediately after brushing your teeth and the antibacterial strength of the hone will help to heal the infections.
- Cranberry Juice
It has been used in the past for treating different infections. It can also be used to treat gum infections due to its ability to stop the bacteria from attaching itself to the teeth. In doing this, using unsweetened cranberry juice will be more effective.
- Vitamin C
Lemons are rich in vitamin C, and this helps them to control the influx and growth of gum diseases. Any food rich in vitamin C can be used for the treatment of gum infections. The antioxidant properties of vitamin C help in regenerating weakened bones and also in the growth of tissues. They also help to improve oral health generally.