Bladder Function
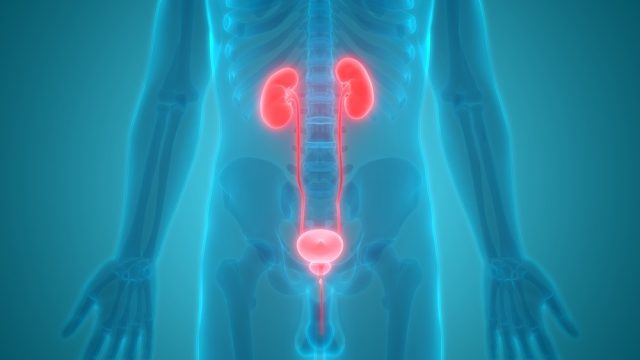
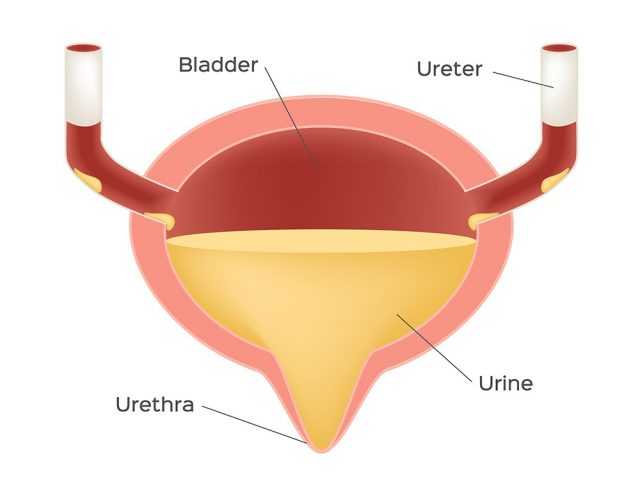
A urinary bladder functions as the body’s storage tank for urine. It is a hollow and elastic organ which stores the urine produced by the kidneys. This urine produced by the kidneys flows via the ureters in to the bladder.
After it’s full, the urine passes through the urethra and exits the body. It controls and delays the process of urination and works to make a normal person urinate in large amounts several times in a day instead of leaking small amounts continuously.
Anatomy
It possesses an almost spherical shape and its size varies in different individuals. The size and shape also depends on the volume of stored urine inside. It is located anterior to the rectum in the pelvic cavity and superior to the reproductive organs in men.
In females, it is a little smaller in size as it must share the space in the pelvic cavity with the uterus. When a woman is pregnant, the uterus enlarges and puts pressure on the bladder and so the woman urinates often.
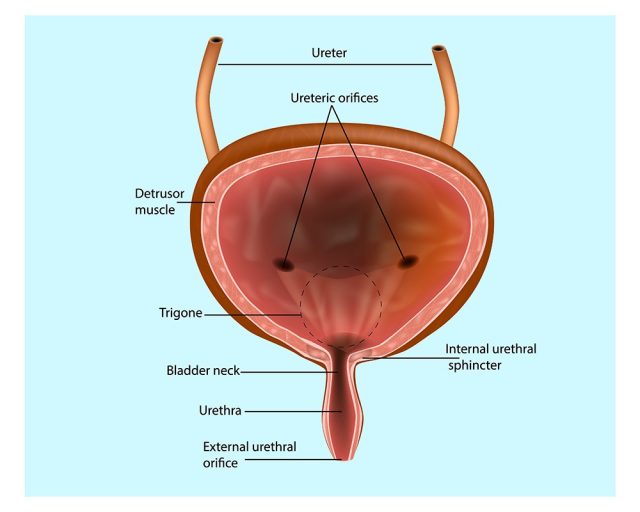
Tiny wrinkles called the rugae are found in the inner lining of the bladder which allow the bladder to stretch as the urine fills up. Ureteral openings from both the kidneys allow the urine to enter a hollow lumen. This lumen or the urinary bladder has a small funnel like opening at its inferior end leading to the urethra.
The urinary bladder consists of different layers of tissue:
- Mucosa layer forms the innermost layer lining the hollow organ. The mucosa lining the urinary bladder is additionally lined with transitional epithelial tissue that can stretch to store large volumes of urine. This tissue also protects the bladder from alkaline or acidic urine.
- Next comes the submucoal lining which is actually a connective tissue layer consisting of nervous tissue and blood vessels which control and support the other surrounding layers.
- The submucosa is next lined with a layer of visceral muscles which provide the bladder the ability to contract and expand. This visceral muscle layer is called as muscularis and is also called detrusor muscle. The muscularis form the internal urethral sphincter surrounding the urethral opening. It holds the urine in the bladder and relaxes to allow the outflow of urine.
- Due to the positioning of the urinary bladder in the abdominopelvic cavity, its outermost layer consists of serous membrane which protects the bladder against friction between organs in the cavity.
- The inferior and lateral sides of the bladder has a layer of a loose connective tissue namely adventitia. This tissue connects the bladder to the tissues surrounding the pelvis.
Urinary Bladder function
It functions as a vessel to store urine and to delay urine frequency. The organ is the most elastic in the body and it can accommodate around 600 to 800 ml of urine at a given time. Various tissues like the visceral muscle tissues, elastic fibers and the transitional epithelium help the bladder in its elasticity and to be able to contract to the original size many times in a day.
The contraction of the detrusor muscles in the bladder enables it to expel urine from the body by contracting and the relaxing of the internal urethral sphincter which acts like a valve. The external urethral sphincter helps to delay and control the urination by its contraction ability. This one is a skeletal muscle which allows one to control the urine.
Diseases in the urinary bladder
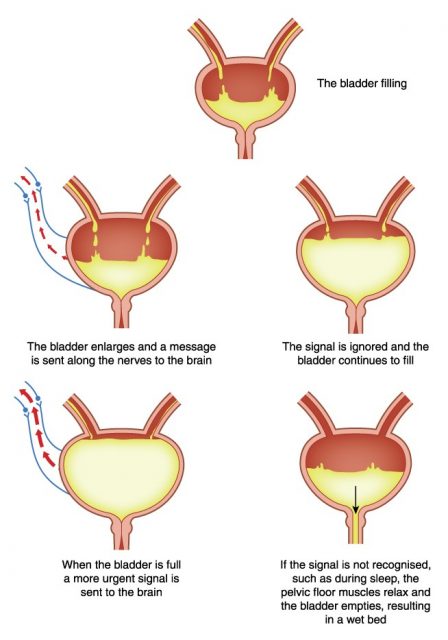
The most common urinary bladder problem is the frequent urge to pass urine and bladder incontinence that is the leakage of urine from the bladder. Due to the decreased capacity of the bladder muscles, leakage and frequent urine urges result. The decreased capacity of the bladder is the result of problems like constipation, excessive caffeine and other bodily complications. Bladder spasms or stress also result in leakage of urine.
Frequent urination for men happens mostly during nights disturbing their sleep. This happens due to incomplete emptying of the bladder. An enlarged prostate hinders the complete emptying of the bladder.
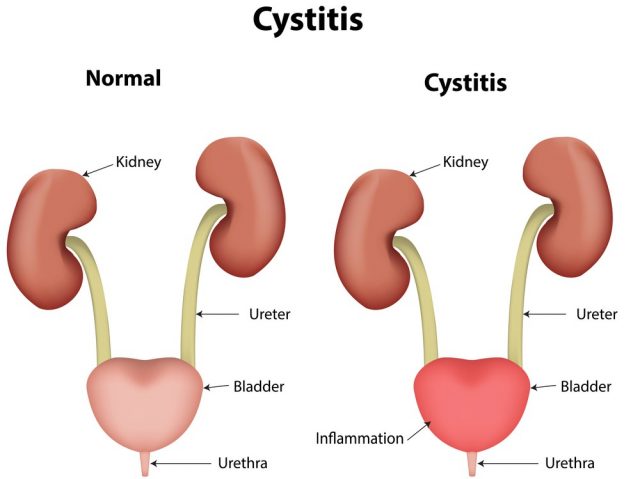
Another reason for frequent urination could be infections in the bladder. Infections like cystitis are the result of bacteria and are the most common infection which affects the bladder. One-third of women are suspected to get bladder infections at least once in their lives.
They experience pain and burning during passing urine. They get the urge to urinate but are able to expel only a small amount each time. They also get lower abdominal pain, a sudden painful need to urinate and bloody or cloudy urine.
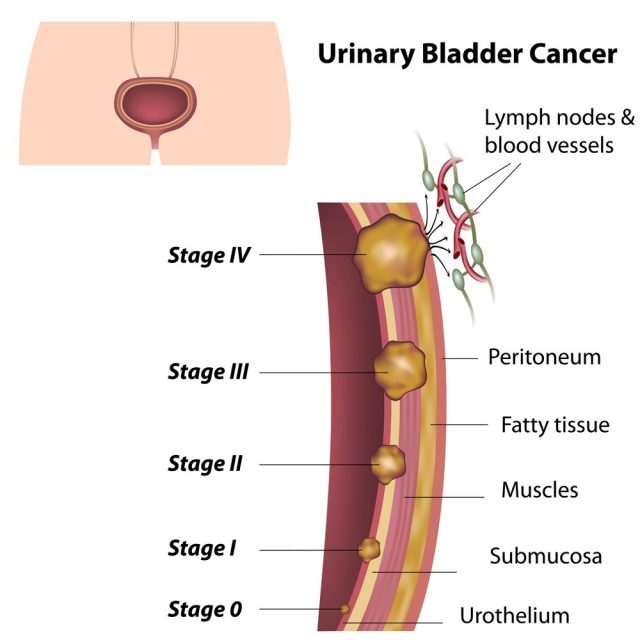
A deadly bladder condition is bladder cancer. It affects people who are older generally, but in some occurrences, younger people also have been affected with bladder cancer. One can get blood in the urine, painful urination, frequent urination and pelvic and lower back pain due to bladder cancer.
Some females get affected with prolapsed bladder also called the cystocele. Due to strain, sometimes, the tissue between the vaginal walls and a woman’s bladder weaken which allows the tissue to stretch and bulge right into the vagina.
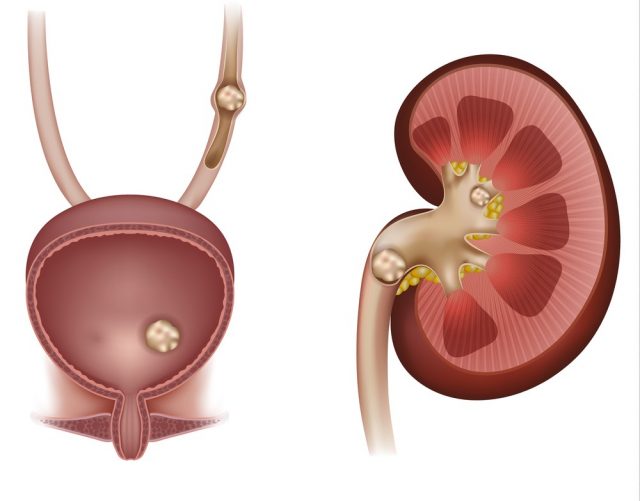
Sometimes, concentrated urine results in bladder stones which crystallize in bladder. Bladder stones are another common problem in men and women. A person having bladder stones is unable to empty the bladder in one go.
Repeated occurrences of holding the urine result in over-expansion of the bladder, the transmission of excess pressure into the kidneys and inability to completely empty the bladder. Holding the urine for long result in cystitis, urinary tract infections and deterioration of the kidney and bladder function.
Women also get bladder infections after menopause when estrogen levels drop in their body. This leads to thinning of the urethral lining and also changes the bacterial balance in the vagina leading to infections in the bladder.
Pregnant women also get bladder infections due to the enlargement of the uterus which puts pressure on the bladder and also prevents it from emptying completely at one go. This causes the bacteria to thrive inside.
Bladder Function Tests
The doctor may prescribe a urodynamic test for checking a person’s bladder function. It helps to diagnose the cause of incontinence or any other bladder infection.
The person is instructed to fill his bladder by drinking lots of liquid. The bladder is then emptied and the pressure readings are taken from the bladder and the tummy. In this test, the symptoms are replicated to determine the cause of the infection.
The tests are used to diagnose:
- Urge urinary incontinence: In this condition, there is a sudden urge to urinate and the urine at times leaks before a person could reach the bathroom. The bladder muscles contract too early.
- Stress urinary incontinence: This is the common problem in bladder. The pressure at times becomes too much for the outlet of the bladder to withstand because the pelvic floor muscles have weakened. This causes leakage of urine. The person gets this type of incontinence whenever he or she laughs, cries or exercises.
- Mixed urinary incontinence: This is a mixture of both stress and urge incontinence.
With the results, the doctors may be able to identify other underlying causes of infection. If the doctor is considering surgery for the patient, then a urodynamic test is done to ascertain certain readings.
Initially, in this test, the amount of urine which leaves the bladder is noted down for a particular time period. After noting down the flow rate, abnormalities in the flow rate are ascertained. A decreased flow rate indicates problems with the emptying of the bladder and this could be due to faulty muscle functioning of the bladder.
Next, a filling cystometry is done in which thin catheters are inserted in the bladder and the rectum to measure the pressure of the bladder and the abdomen as the urine fills in the bladder. Pressure readings are taken with this test. If there is leakage without any pressure issue, then the problem is detected as stress incontinence and if the pressure is found to be increasing leading to leaking, then it is diagnosed as urge continence.
After the tests, the person might feel a burning sensation while passing urine but these symptoms quickly settle down after drinking a lot of fluids. After a urodynamic test, one may get urinary tract infection due to the insertion of thin tubes in the bladder.
But this can be prevented if the person drinks enough fluids after the test which will flush out the bacteria. A person is also advised to cut down on coffee and tea until the bladder returns to normal. The person is instructed to drink juices, coconut water and other herbal drinks to normalize the urinary system. Also, the person is instructed to try to void for longer period to make sure that the bladder is emptied thoroughly.
Urinary bladder infections are curable and one should take medical help if the person feels some problems with their urination. This problem if left untreated could lead to severe complications in the body.